1.Product Definition
Sodium 3-chloro-2-hydroxypropylsulfonate (CHPS-Na) is an organic compound with CAS No.126-83-0, a molecular formula of C3H8ClNaO4S, and a structural formula of: 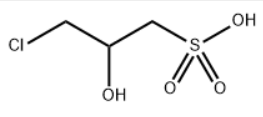
It appears as white powdery crystals, slightly soluble in water with a solubility of 405g/L.
2. Product Applications
CHPS-Na is an important organic chemical intermediate. Because its molecular structure contains both hydrophilic sulfonic acid groups and highly active halogen atoms, it is widely used in the preparation of surfactants, starch modification, printing and dyeing protective agents, and drilling fluid fluid loss control materials.
CHPS-Na can be alkylated with amides to produce amphoteric surfactants containing sulfonic acid groups. Research results show that sulfonic acid-containing amphoteric surfactants are temperature- and salt-tolerant, and highly active. Under alkaline conditions, CHPS-Na can be etherified with starch to produce 2-hydroxy-3-sodium sulfonate propyl starch ether, a sulfonic acid-containing starch derivative. This sulfonic acid-containing starch derivative is an excellent drilling fluid fluid loss control material.
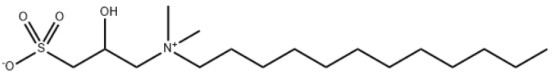
Amphoteric sulfobetaine surfactant is produced by quaternizing a long-chain alkyl tertiary amine, sodium 3-chloro-2-hydroxypropylsulfonate, and a catalyst in aqueous solution. This amphoteric surfactant exhibits excellent softening, smoothing, and antistatic properties on fabrics, along with certain bactericidal and mildew-inhibiting properties. It also possesses good emulsifying and dispersing properties.
Lauryl Hydroxysulfobetaine, codenamed LHSB and CAS number 13197-76-7, is a light yellow, transparent liquid. It can be used as a surfactant. It is mildly irritating to skin and eyes, exhibits good foaming properties and stability, and exhibits excellent hard water resistance.
Under alkaline conditions, CHPS-Na forms highly active sodium propylene oxide sulfonate, which then undergoes an etherification reaction with starch molecules to produce SHPS, introducing hydrophilic sulfo-2-hydroxypropyl groups onto the starch molecules. As the CHPS-Na dosage increases, the number of CHPS-Na molecules available to react with active sites on the starch chain increases, enhancing the degree of modification in the etherification reaction.
2-Hydroxy-3-sulfopropyl starch ether (HSPS) is a green chemical synthesized from corn starch. It is used in oilfield production to stabilize wellbore walls, flocculate drill cuttings, and reduce fluid loss. It also exhibits certain heat, salt, and calcium tolerance properties.
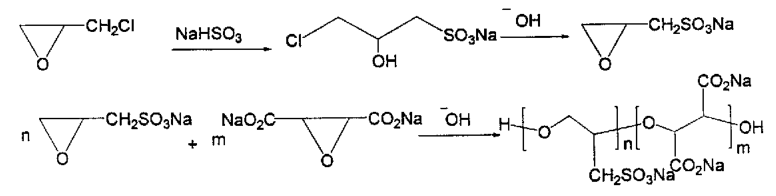
Literature reports that sodium 2,3-epoxypropanesulfonate is produced by reacting sodium 3-chloro-2-hydroxypropanesulfonate with sodium hydroxide. This is then copolymerized with epoxysuccinate in the presence of calcium hydroxide as an initiator to produce polyepoxysulfonic acid (PECS). PECS is a scale inhibitor that inhibits calcium phosphate deposition, stabilizes zinc salts, and disperses iron oxide. The synthesis route is shown below: